Hair loss in women can be a distressing experience, impacting confidence and self-esteem. Understanding its causes and potential treatments is crucial. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into female pattern hair loss (FPHL), exploring its various aspects and offering practical solutions for prevention and management, including addressing alopecia causes in females.
Alopecia Causes in Females
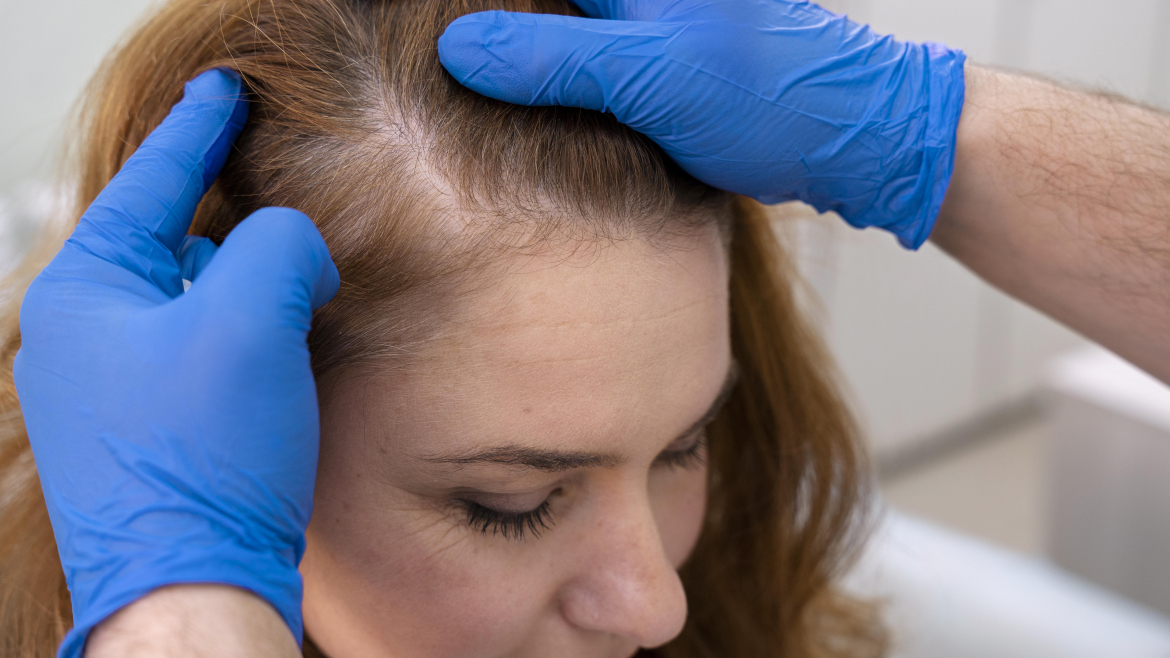
Female Pattern Hair Loss(FPHL) is the most common type of hair loss in women, affecting about one-third of susceptible women, equating to approximately 30 million individuals in the United States. FPHL is characterised by the thinning of hair along the top of the head, leading to noticeable hair loss.
Causes of FPHL and Alopecia in Females
Genetics
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in FPHL and alopecia. If your immediate family members have experienced hair loss, you are more likely to be susceptible.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal imbalances, especially during menopause when estrogen levels decrease, can lead to FPHL and alopecia in females. Androgens, the male hormones, can have a more significant impact, causing hair follicles to shrink and hair to thin.
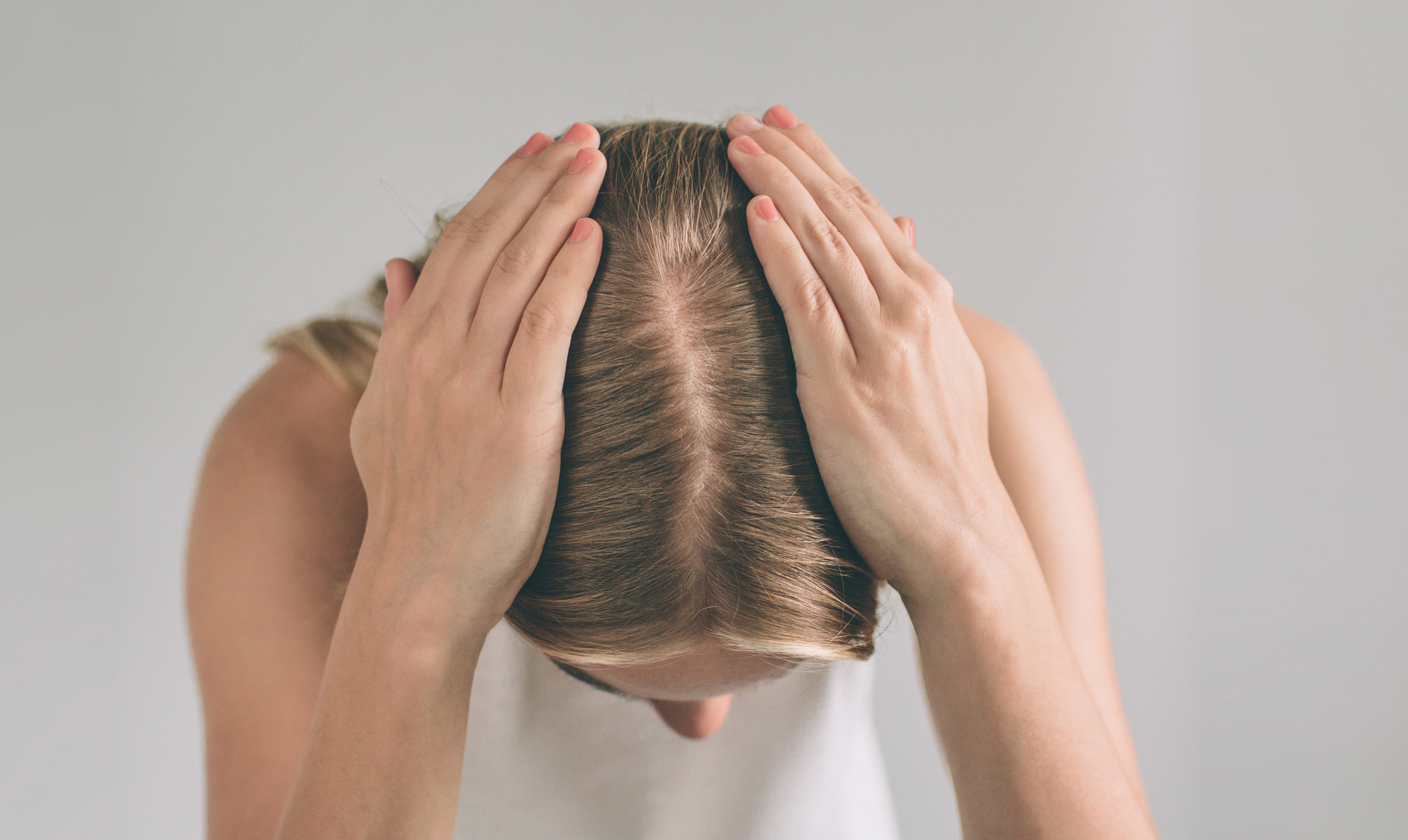
Identifying FPHL and Alopecia: Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs of FPHL and alopecia is vital for timely intervention:
Increased Daily Hair Shedding: Finding more than 125 hairs daily on your brush, pillow, or in the shower.
Thinning Hair: Noticeable patches of thinner or missing hair, especially on the top of the head.
Weakened Hair: Hair becoming finer and more prone to breakage.
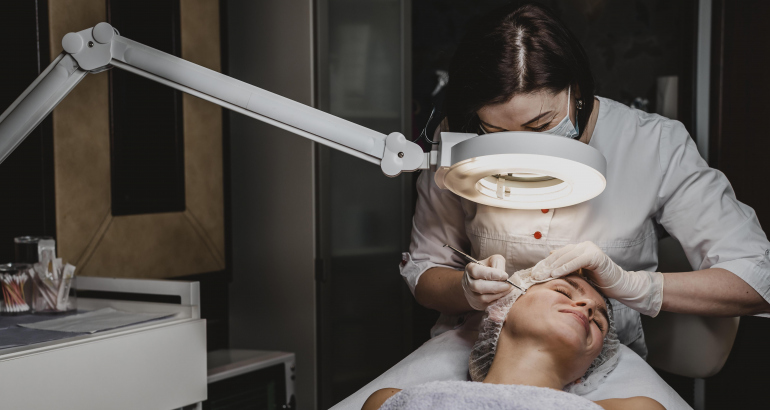
 Diagnosis and Tests
Diagnosis and Tests
When consulting a healthcare provider for hair loss, several diagnostic methods are employed:
Physical Examination: The healthcare provider examines the scalp and hair to assess the extent and pattern of hair loss.
Blood Tests: Checking vitamin, mineral, and hormone levels to identify deficiencies or imbalances.
Scalp Biopsy: A small piece of scalp skin is examined to understand the underlying causes.
Treatment Options for FPHL and Alopecia
Lifestyle Changes
Avoiding Hair Damaging Practices: Refraining from hairstyles like tight braids or ponytails that cause traction alopecia, a significant contributor to hair loss.
Balanced Diet: Ensuring a diet rich in essential nutrients like vitamins D and B, zinc, and protein supports overall hair health.
Medical Interventions
Topical Minoxidil (Rogaine): An FDA-approved treatment stimulating hair growth. It needs consistent application following directions.
Low Light Laser Therapy: Devices like HairMax Lasercomb® and Theradome LH80 PRO® stimulate hair follicles, promoting growth.
Hair Transplant Surgery: Transplanting hair follicles from the back of the head to bald areas, offering a long-term solution.
Future Possibilities
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Injections: Concentrated platelets from the patient’s blood are injected, encouraging hair growth.
Micro needling with Minoxidil: Enhancing the effectiveness of minoxidil by combining it with micro needling.
Conclusion
Female Pattern Hair Loss and alopecia are common concerns, but with advancements in treatments and a proactive approach, managing and even regaining lost hair is possible. By understanding the causes, recognizing the signs, and exploring suitable treatments, women can regain confidence in their appearance. If you’re experiencing hair loss, consult a dermatologist promptly to explore the most effective solutions tailored to your needs.